What are keloid scars?
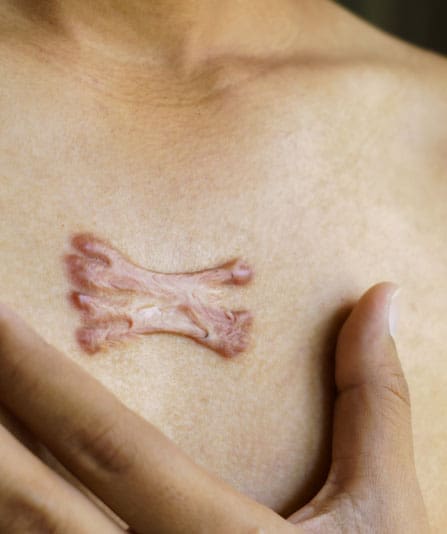
Keloid scars share similarities with regular scars in their shiny, firm, and smooth appearance. They are a type of raised scar that forms as a result of an overgrowth of scar tissue. They can be distinguished from hypertrophic scars by their tendency to extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound site and their potential to grow larger over time. Keloids can develop anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the earlobes, chest, shoulders, and back.
Keloid scars are a common concern for many individuals, often causing discomfort and self-consciousness. These raised scars can develop due to various factors.
What causes keloid scars?
Keloid scars share similarities with regular scars in their shiny, firm, and smooth appearance. They are a type of raised scar that forms as a result of an overgrowth of scar tissue. They can be distinguished from hypertrophic scars by their tendency to extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound site and their potential to grow larger over time. Keloids can develop anywhere on the body but are commonly found on the earlobes, chest, shoulders, and back.
Keloid scars are a common concern for many individuals, often causing discomfort and self-consciousness. These raised scars can develop due to various factors.
What causes keloid scars?
Whenever an area of the skin is subjected to damage through injury, surgery or inflammation, a scar usually follows. While the scar is being formed, sometimes too much collagen is produced within the scar. Consequently, this results in what is known as a hypertrophic scar – a raised scar which is itchy and looks a little red (or dark). In extreme cases, these hypertrophic scars become keloid scars. The main difference between hypertrophic scars and keloids is that the latter spreads to the surrounding areas of the injured skin and does not regress.
The exact cause of keloid formation is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic, environmental, and wound-related factors. Keloids occur when the body’s normal wound-healing process goes awry, leading to an overproduction of collagen and the formation of excessive scar tissue.
Factors contributing to the development of keloid scars
Several factors can increase the risk of developing keloids, including:
- Genetic predisposition: Individuals with a family history of keloids are more likely to develop them themselves, suggesting a genetic component to their formation.
- Skin injuries: Any type of cutaneous injury, such as acne scars, body piercings, or surgical incisions, can trigger keloid formation.
- Skin tension: Wounds that are under tension during the healing process are more likely to develop keloids, particularly on areas of the body with tighter skin, such as the anterior chest.
- Chronic inflammation: Persistent inflammation in the skin can contribute to keloid development, as it disrupts the normal wound healing process.
- Darker skin tones: People with darker skin are more susceptible to the formation of a keloid scar, possibly due to differences in collagen synthesis and blood flow.
Treatment Options for Keloid Scars
It is important to note that keloid scars cannot be completely eliminated once they appear, however, there are several options available to help manage their appearance and symptoms. To work out the best course of action, a skin biopsy could provide valuable information regarding any skin injury or surrounding skin that might be impacted.
Some of the favoured options when treating keloid scars are a steroid injection, a silicone gel pad, surgical excision, or laser therapy. Which treatment method is likely to get you closer to healthy skin is for you and your surgeon to agree on.
The keloid treatment you opt for is likely to help reduce inflammation and flatten keloid scars over time. If the keloids treated require the surgical removal of keloid tissue, there is a risk of recurrence. There is also laser treatment, radiation therapy, and compression therapy available if you want to improve the appearance of your skin.
Ultimately, many surgical techniques and types of therapy can be used to manage both small keloids and hypertrophic scars.
Preventing keloids
While it may not be possible to prevent keloids entirely, there are steps individuals can take to reduce their risk of developing them.
Avoid unnecessary skin trauma, such as body piercings, or elective surgeries. Also, make sure to treat any skin injuries promptly and follow proper wound care techniques to promote healthy healing. Finally, seek early treatment for any raised scars or abnormal healing responses to minimise the risk of keloid formation.
Keloid scars can be a source of frustration and discomfort for many individuals, but understanding their causes and treatment options can help alleviate some of these concerns. Sometimes you can do everything right, and spontaneous keloids may still appear on the skin surface from no fault of your own.
By addressing keloids early and exploring appropriate treatment modalities, individuals can effectively manage their appearance and improve their quality of life. If you have concerns about keloid scars, consult with a dermatologist or plastic surgeon to discuss the best course of action for your specific situation.
At Goutos London, we have plenty more tips and advice to help with keloid scars and would love to see you at one of our free skin consultations. Get in touch to book yours today.